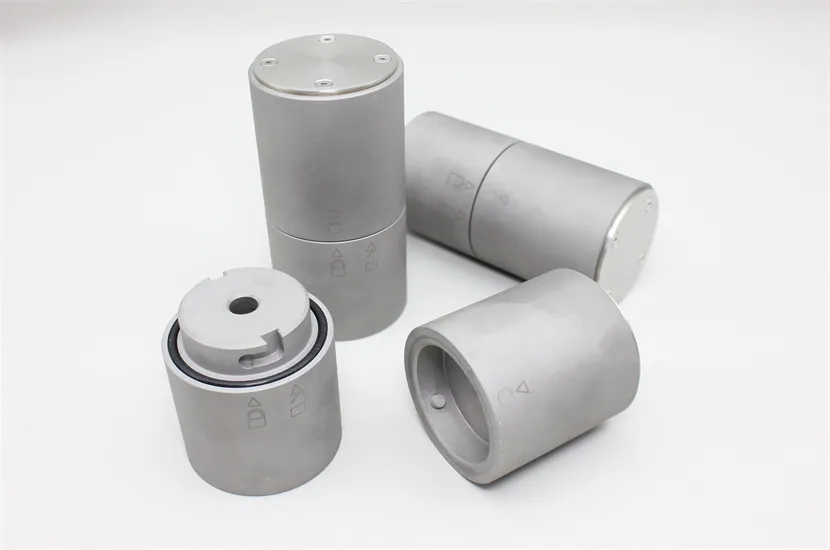
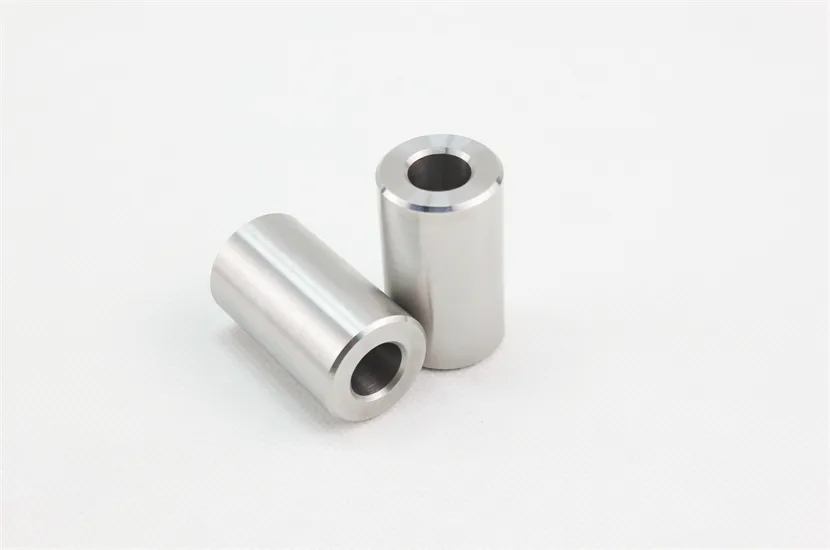
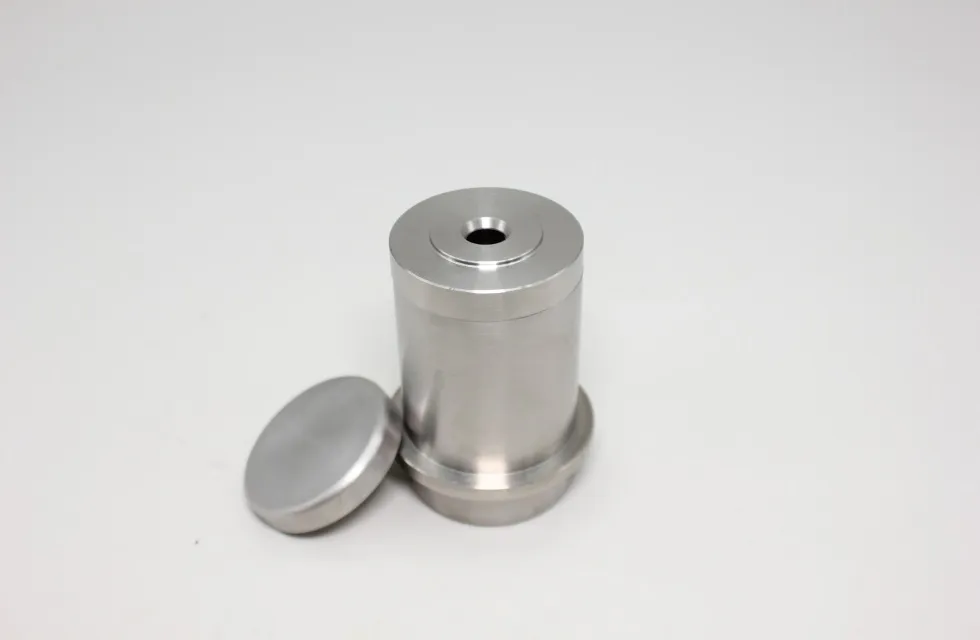
Tungsten nuclear shielding | Professional manufacturer
| Payment Type: | T/T,Alipay etc. |
| Incoterm: | FOB,CIF,EXW,FCA,Express Delivery |
| Min. Order: |
1Piece/Pieces |
Attributes
Model No.: JDTG-TS-019
Brand: ZZJD
Place Of Origin: China
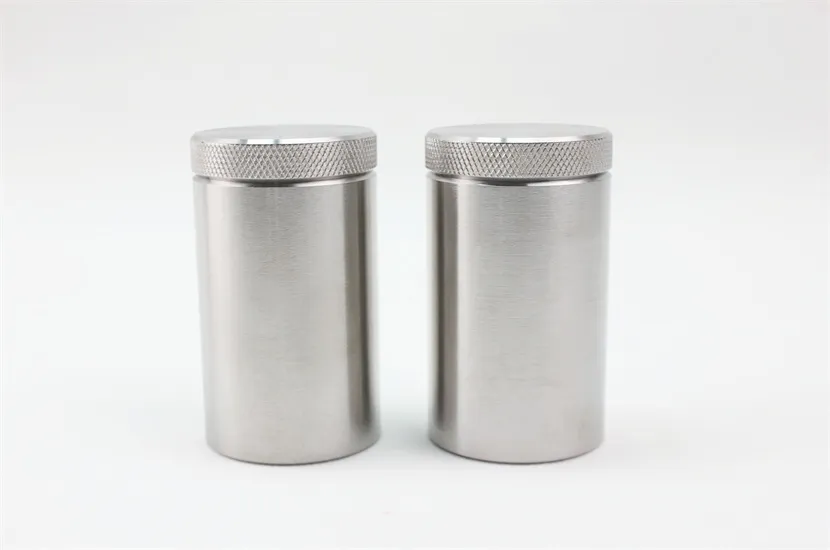
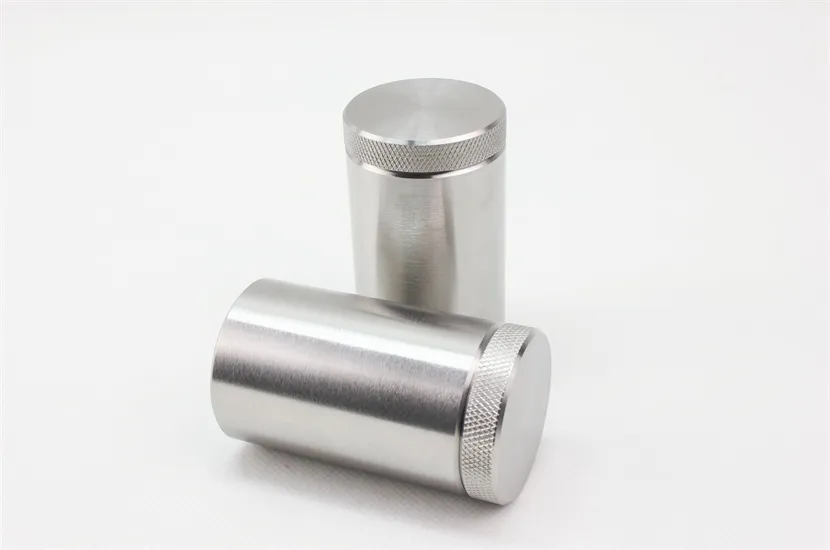
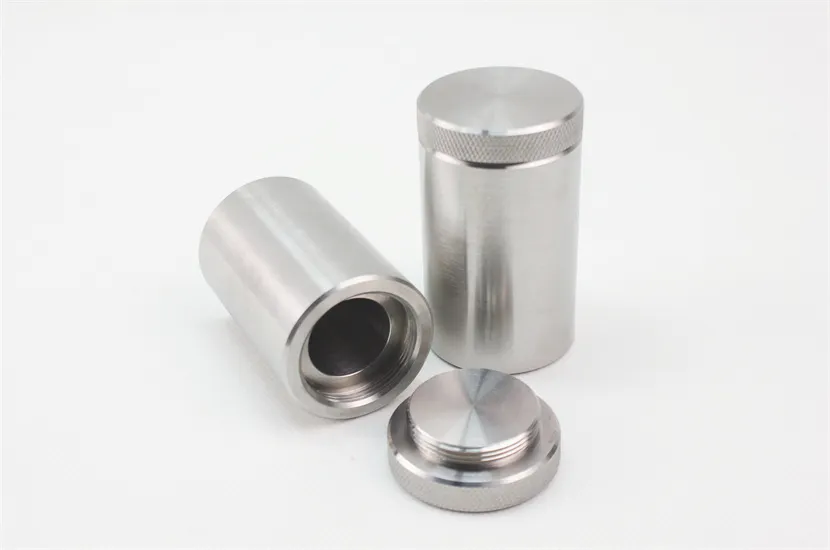
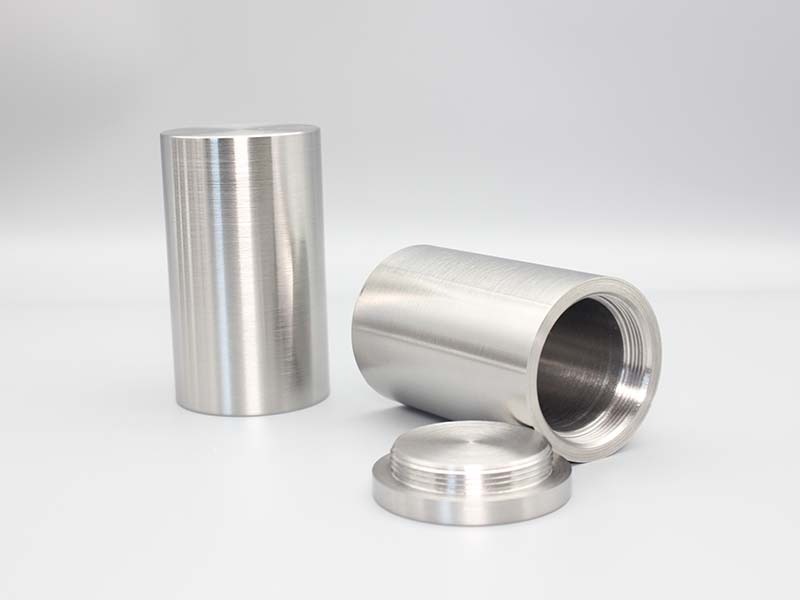
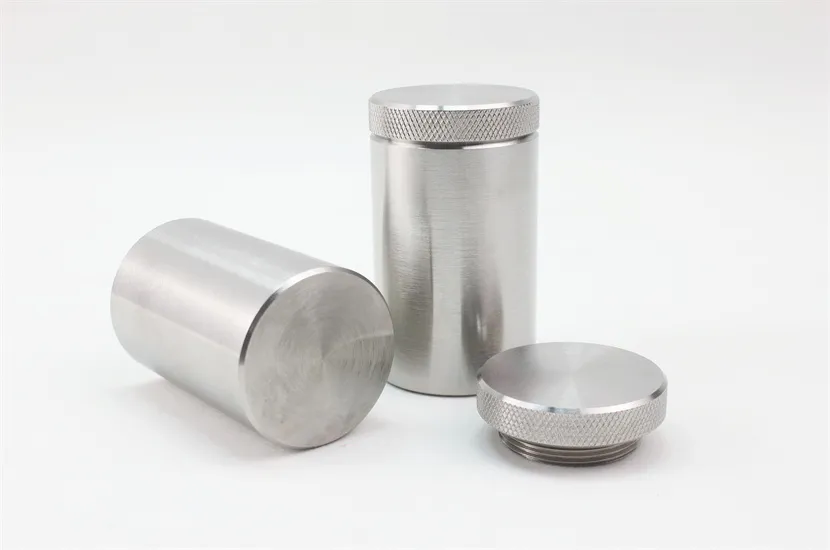
External Dimensions: φ93x130mm
Pit Dimensions: φ33x57mm
Size: 14 KG
Shielding (Tungsten): 29.5mm
Application1: Nuclear medicine
Application2: Medical radiation shielding
Application3: Assisted medical examination
PACKAGING & DELIVERY
Selling Units :Piece/Pieces
Package Type : Standard export packing
DESCRIPTION
Tungsten Radiation Shielding
1. High Density and Atomic Number: Tungsten has a high density (about 19.3 g/cm³) and a high atomic number (74), making it an excellent material for blocking X-rays and gamma rays. These properties allow tungsten to absorb a significant amount of radiation energy, reducing the exposure to people or equipment on the other side of the shield.
2. Applications:
- Medical Imaging: Tungsten is commonly used in medical imaging equipment like CT scanners and X-ray machines.
- Nuclear Medicine: It is used in shielding for radioactive sources used in nuclear medicine procedures.
-Industrial Radiography: In non-destructive testing, tungsten shielding is used to protect workers from radiation during radiographic inspections.
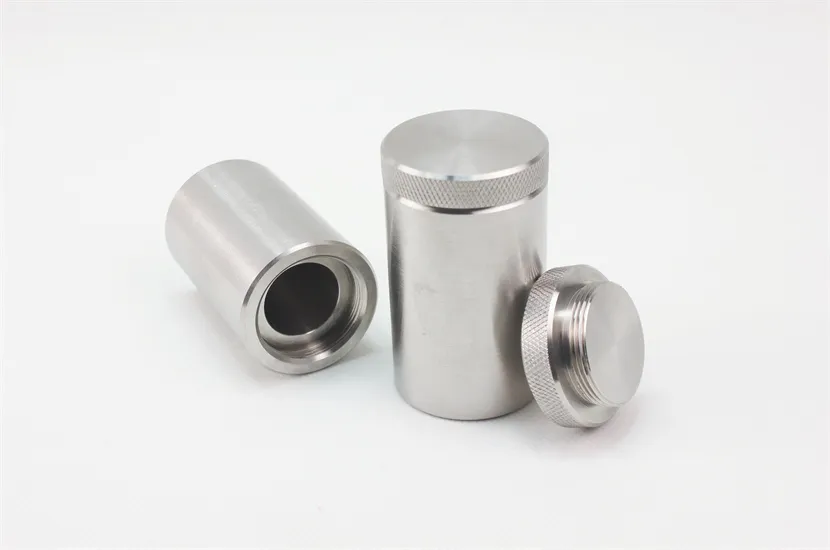

Nuclear Shielding
When we talk about nuclear shielding, we usually mean protection against various types of radiation emitted during nuclear reactions, such as alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, and neutron radiation. Each type of radiation requires a different approach to shielding:
1.Alpha Particles: Easily stopped by thin layers of material like paper or even the dead layer of skin.
2.Beta Particles: Can be shielded with materials like plastic or aluminum.
3.Gamma Rays: Highly penetrating and require dense materials like lead or tungsten for effective shielding.
4.Neutron Radiation: Neutrons are more complex to shield against and typically require materials that capture neutrons efficiently, such as hydrogen-rich materials like water, polyethylene, or borated materials like borated plastics or boric acid solutions.

Tungsten in Nuclear Applications
This small tungsten filter can effectively filter neutrons, reduce unnecessary neutron radiation, and protect key components and workers around the reactor.
With its compact design, this filter element can easily adapt to the complex spatial layout in nuclear fusion reactors. At the same time, the high density and stability of tungsten ensure its long-term reliability in high radiation environments.
While tungsten is highly effective for gamma ray shielding, it may not be the best choice for neutron shielding. Neutron shielding often involves materials that have high hydrogen content or materials that can capture neutrons through nuclear reactions, like boron or lithium.
In summary, tungsten is a great choice for shielding against gamma radiation but might not be ideal for all types of nuclear shielding. The choice of shielding material depends on the specific type of radiation and the environment in which the shielding will be used.

 EN
EN AR
AR FR
FR DE
DE HI
HI IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES ID
ID LV
LV VI
VI HU
HU MS
MS GA
GA BE
BE YI
YI EU
EU





