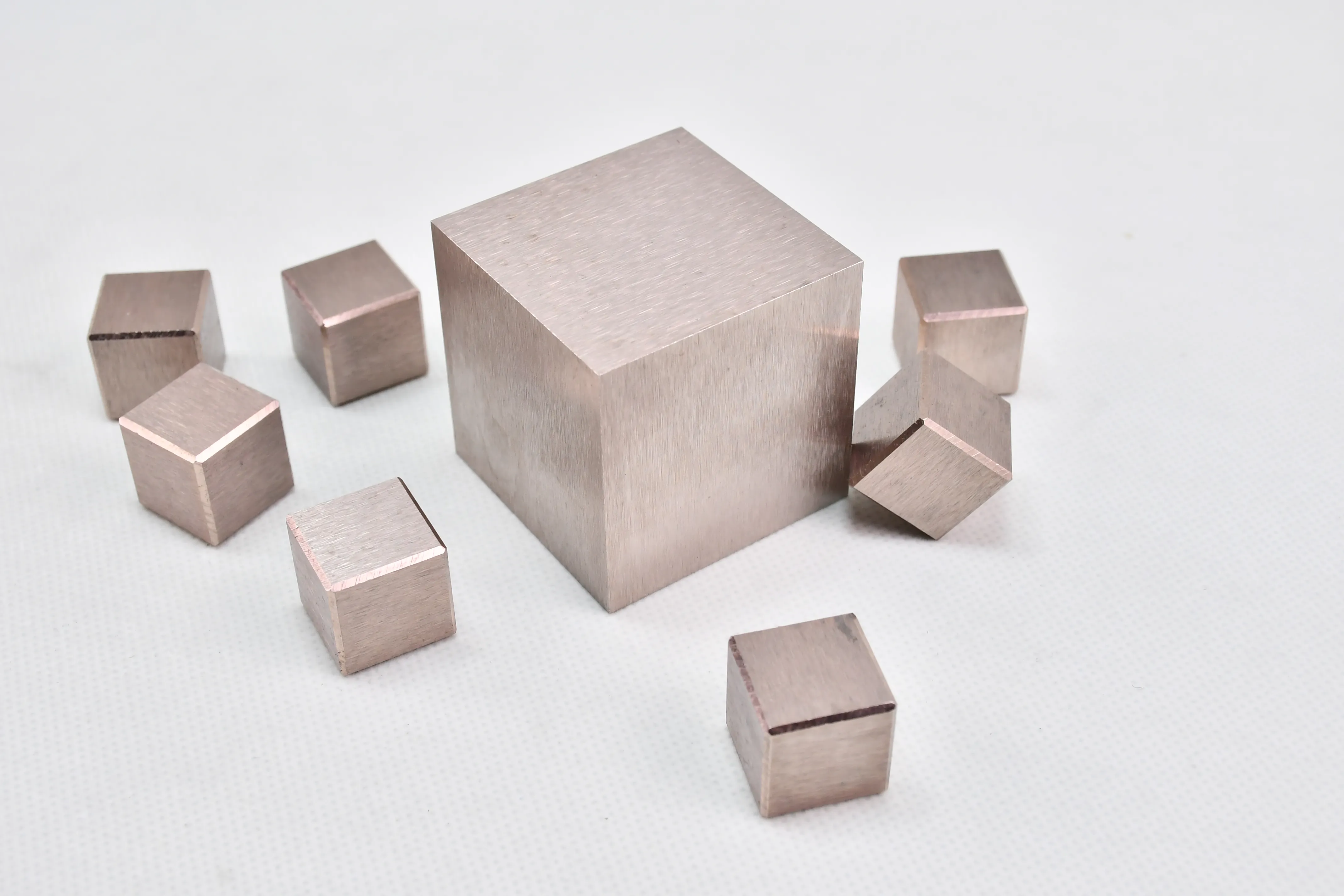
Tungsten Heavy Alloys
Tungsten alloys are usually refractory metals, which are generally composed of W-Ni-Fe (tungsten nickel iron) or W-Ni-Cu (tungsten nickel copper) or W-Ni-Cu-Fe (tungsten nickel copper iron). Some tungsten alloys also add Co (cobalt), Mo (molybdenum), Cr (chromium), etc. They have a high melting point, a density twice that of steel, and are 50% heavier by weight than lead. Tungsten usually accounts for 90% to 98% of the alloy, which is why tungsten alloys have a high density (usually 16.5 grams/cubic centimeter to 18.75 grams/cubic centimeter). Ni, Fe, and Cu are used as adhesives to bond brittle tungsten together, enhancing the ductility of tungsten alloys and making them easy to process; Ni Fe is a commonly used additive, with a ratio of 7Ni: 3Fe or 8Ni: 2Fe (by weight).
The conventional production process of tungsten alloy products includes mixing, cold pressing, and liquid phase sintering until the required density is achieved. During the process of liquid phase sintering, this matrix alloy is in a molten state, which helps tungsten dissolve better in the liquid and disperses large tungsten particles (20-60 microns) into this matrix alloy. This type of material in the sintered state usually undergoes a thermal mechanical treatment process, such as forging, to enhance its hardness and strength. At present, the composition of high density alloys (tungsten alloys) is popular with WNiFe, such as 93W-4.9Ni-2.lFe and 95W-4Ni-lFe. Adding an appropriate amount of cobalt to WNiFe alloy can enhance its strength and ductility. High density tungsten alloys have excellent mechanical properties such as high strength, high hardness, and high wear resistance, as well as good corrosion resistance and thermal stability.
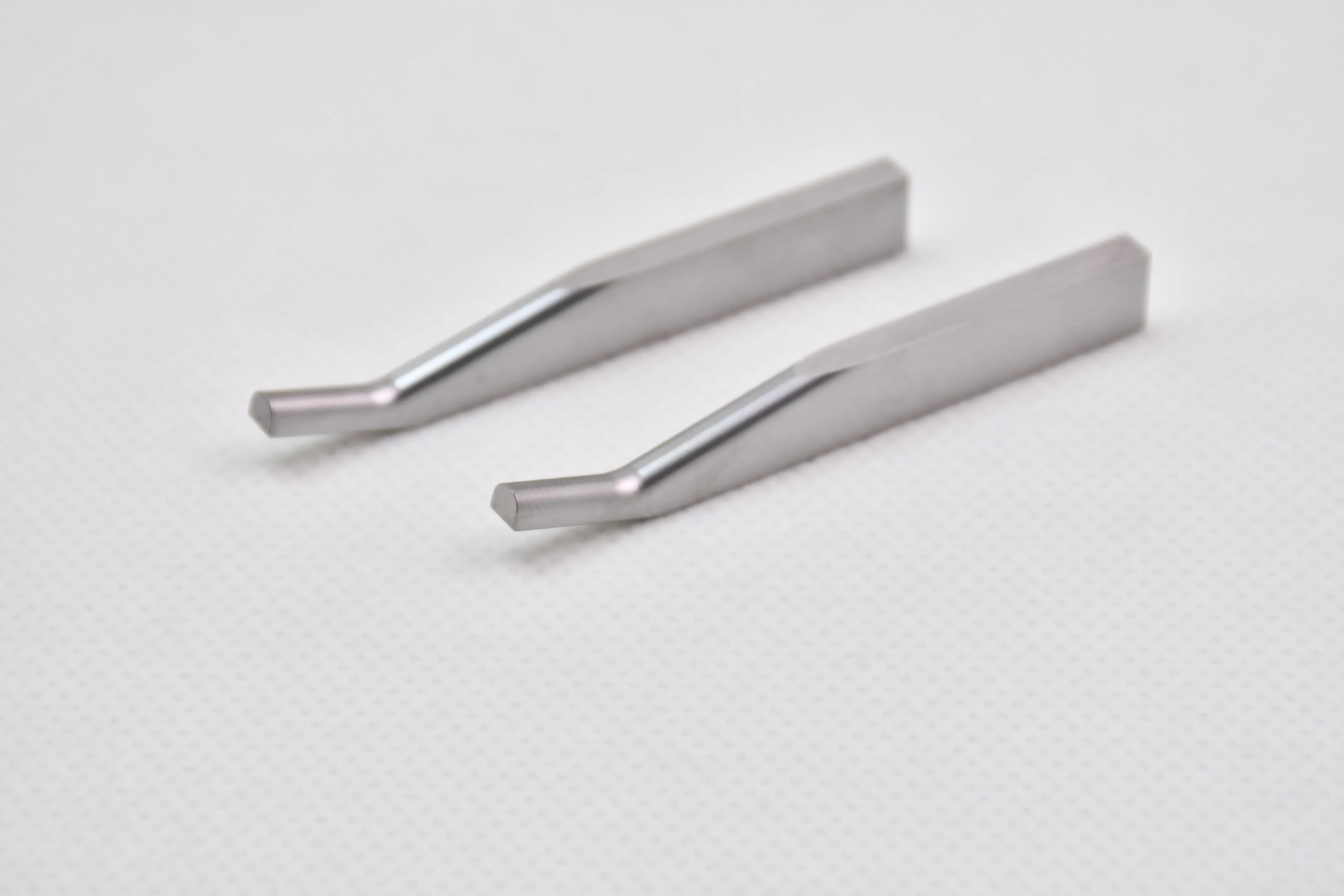
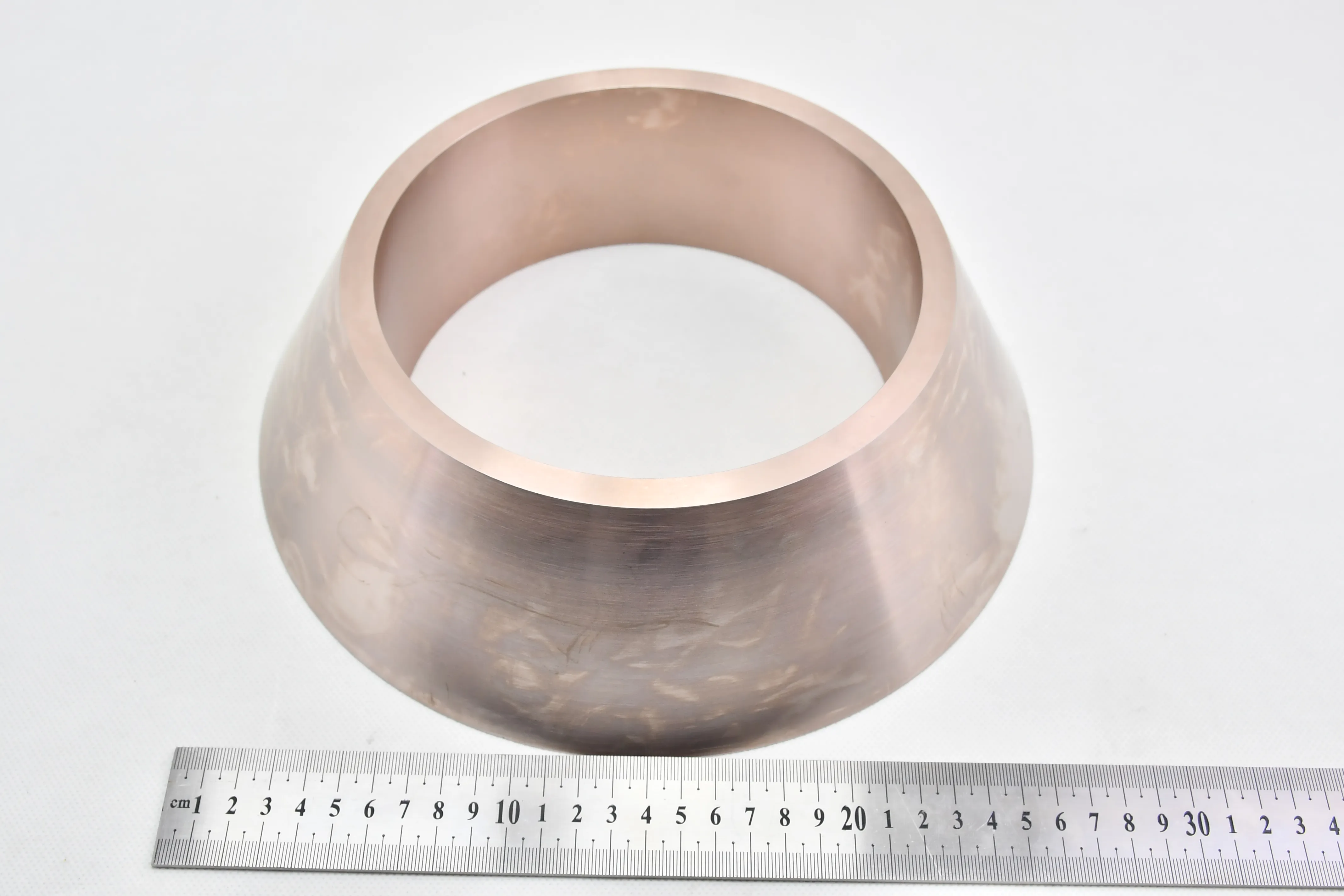
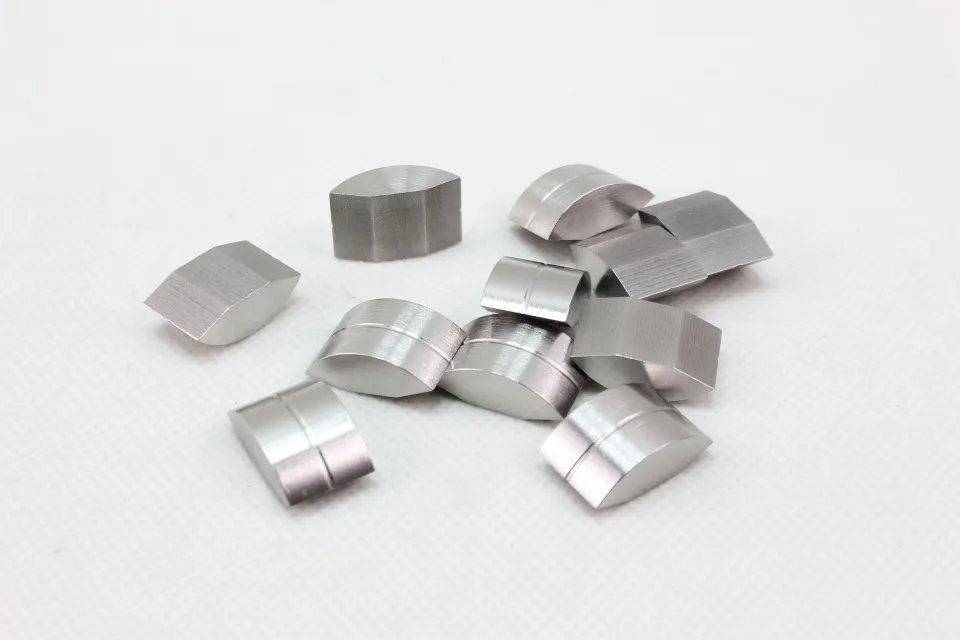
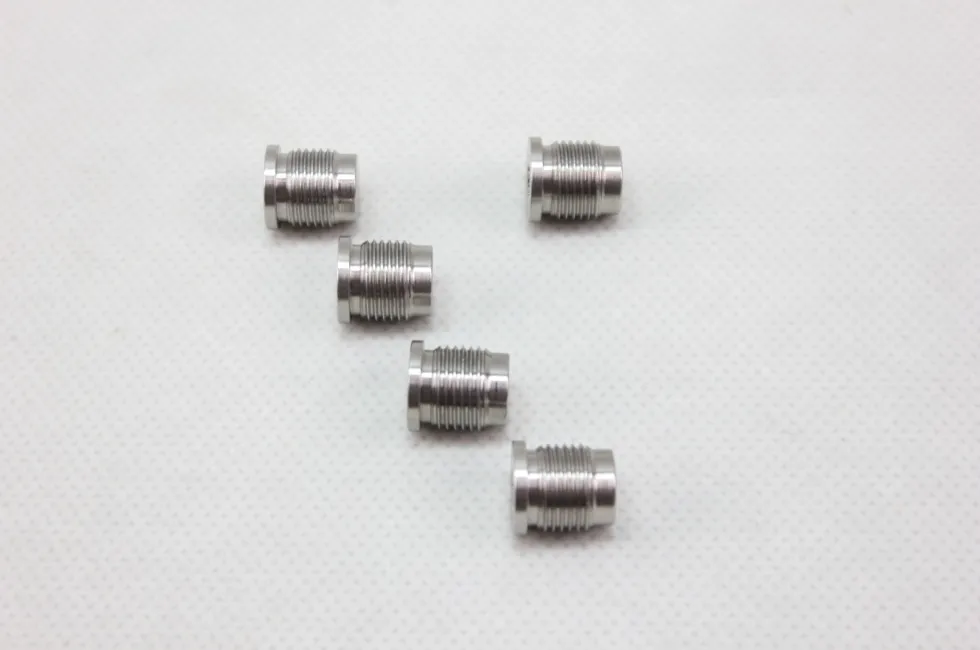
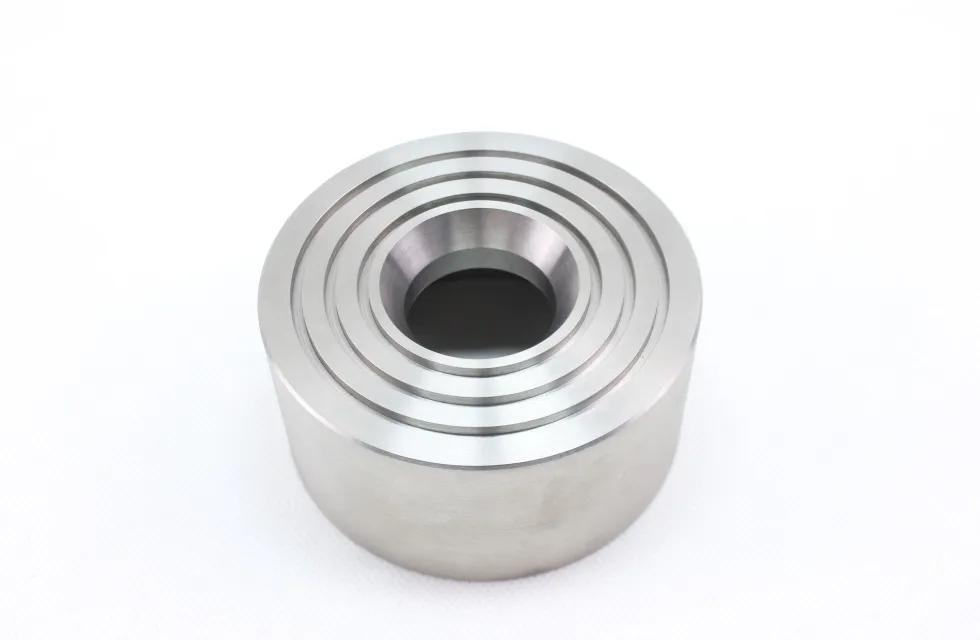
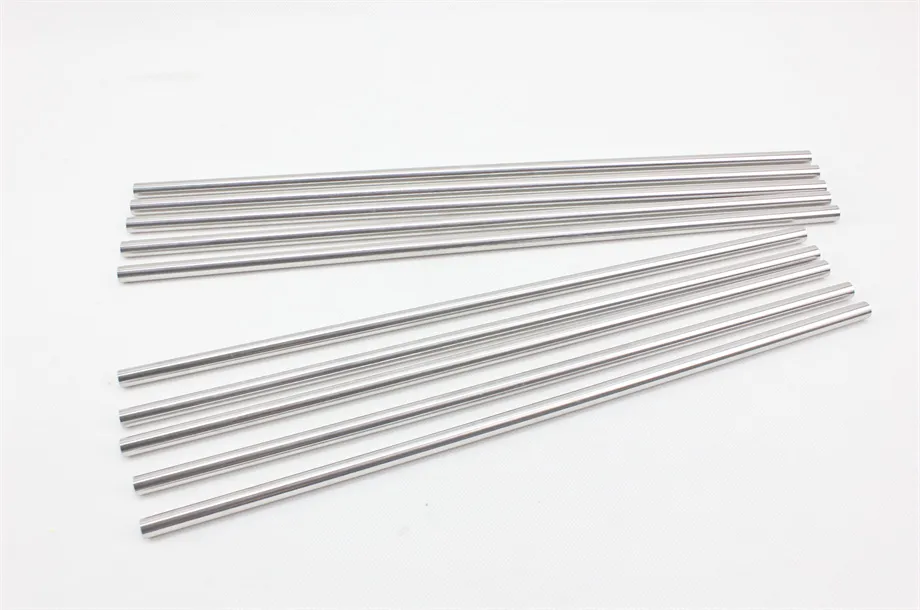
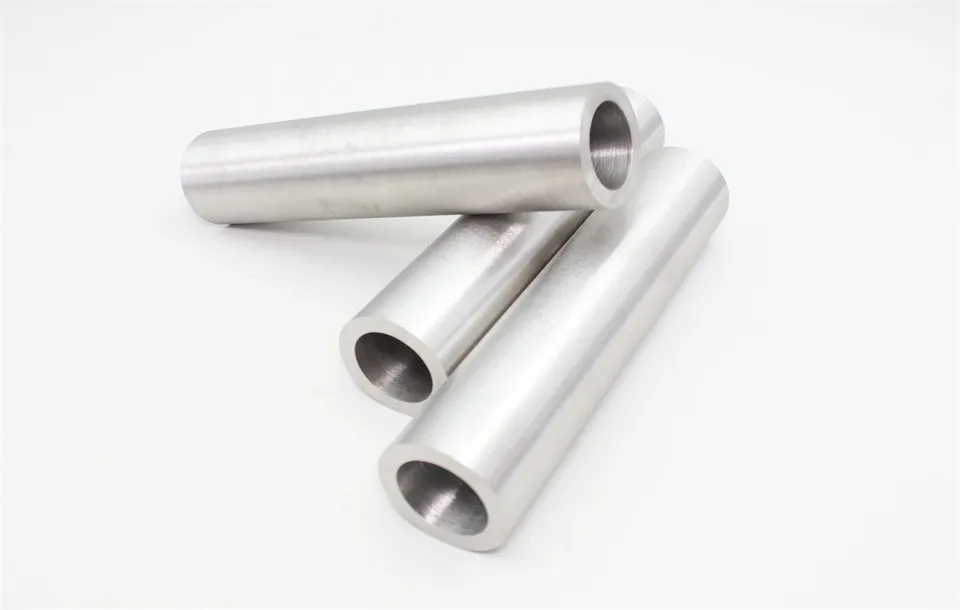
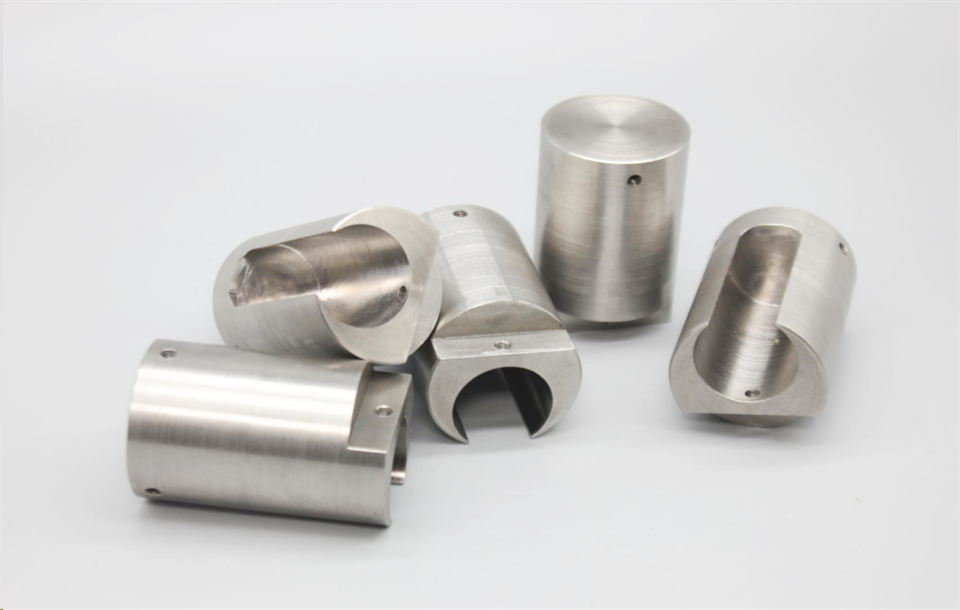
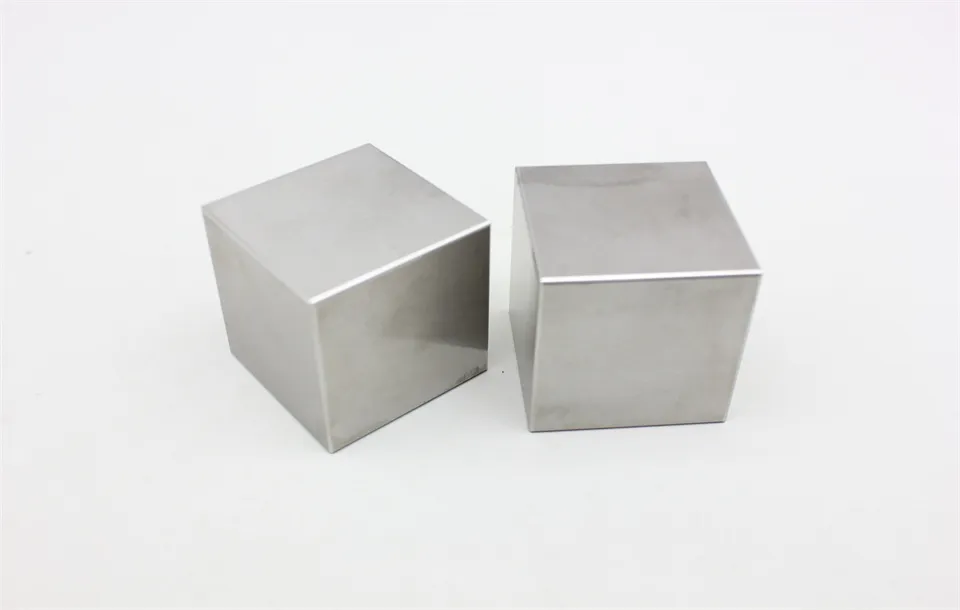
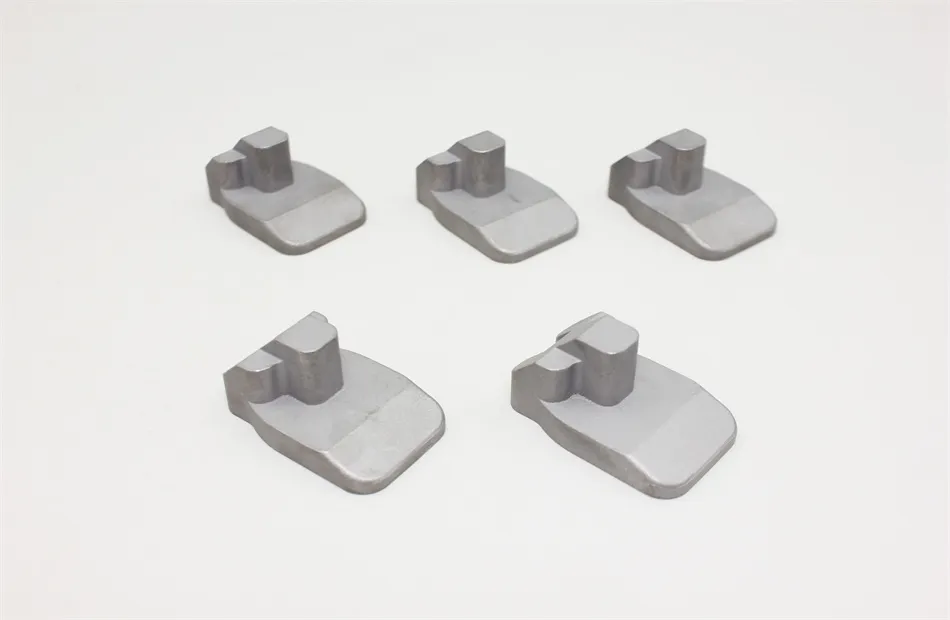
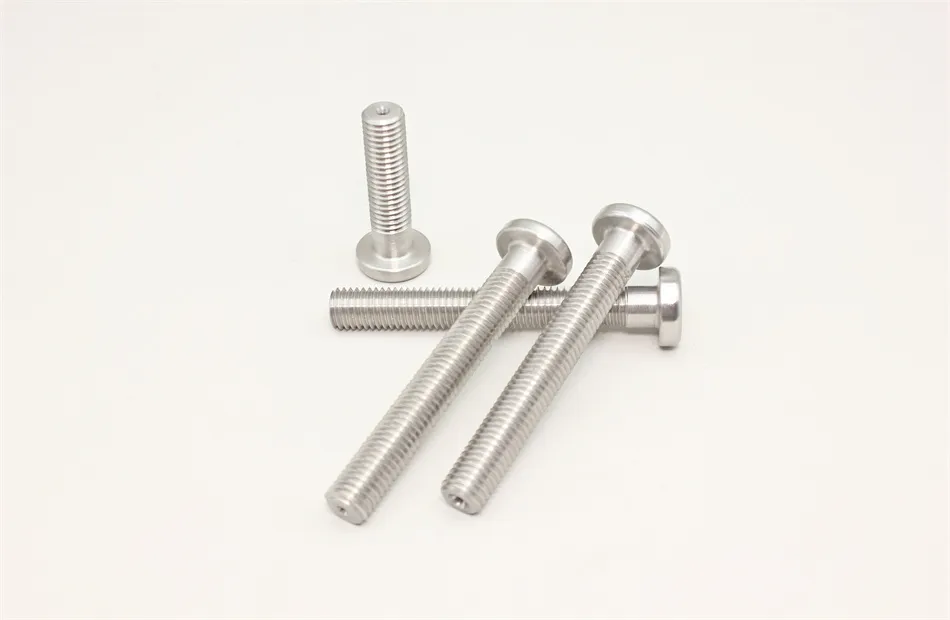
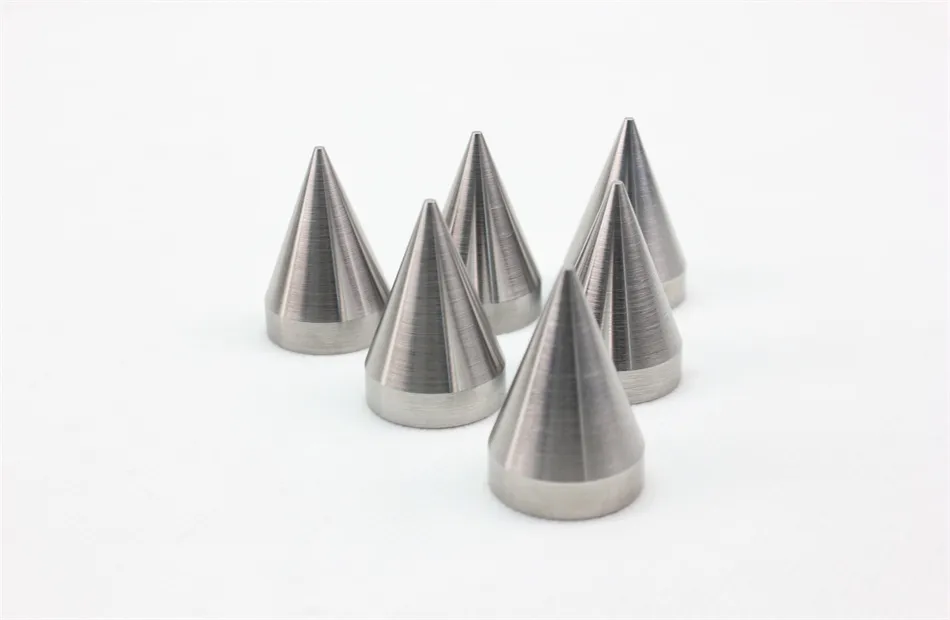
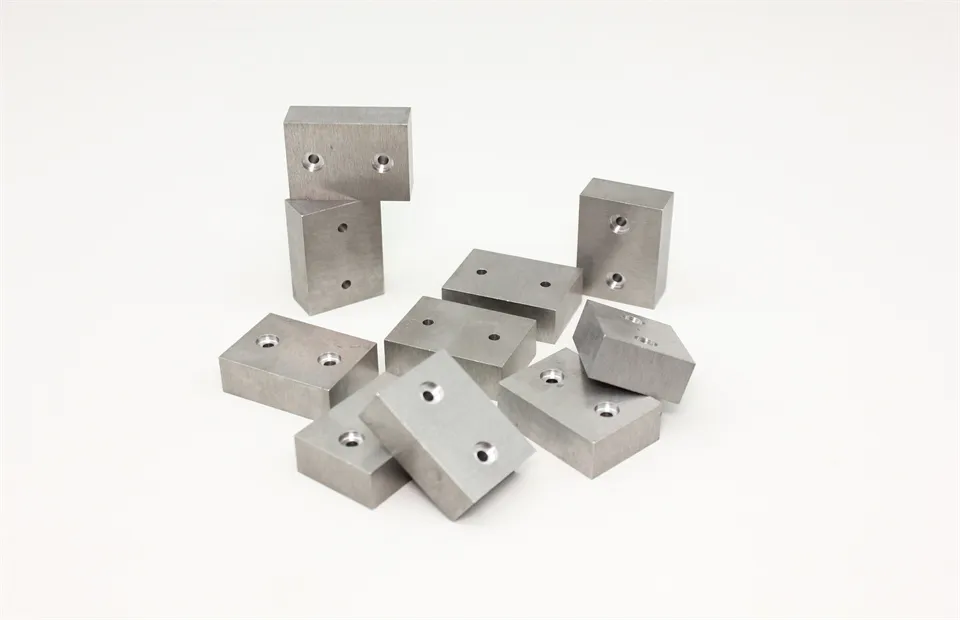
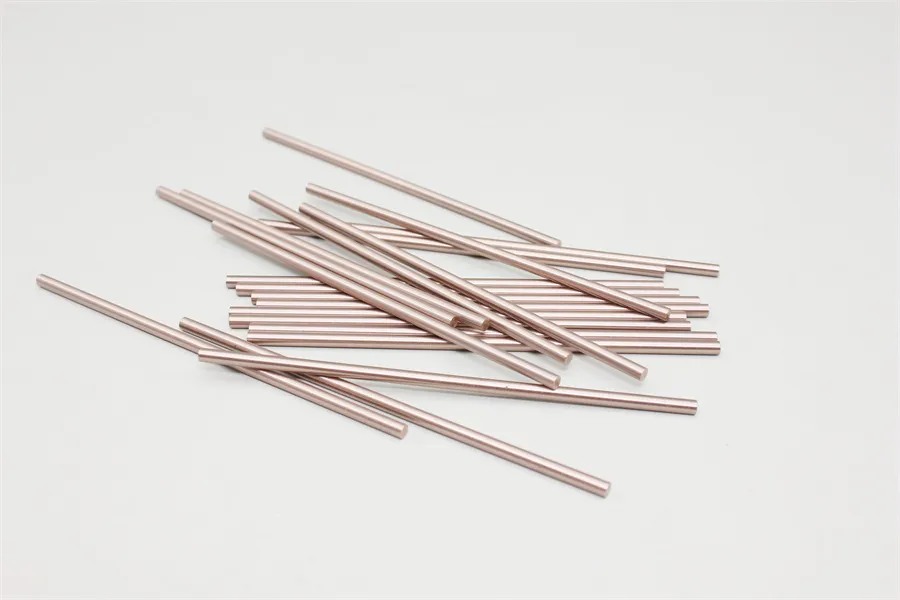
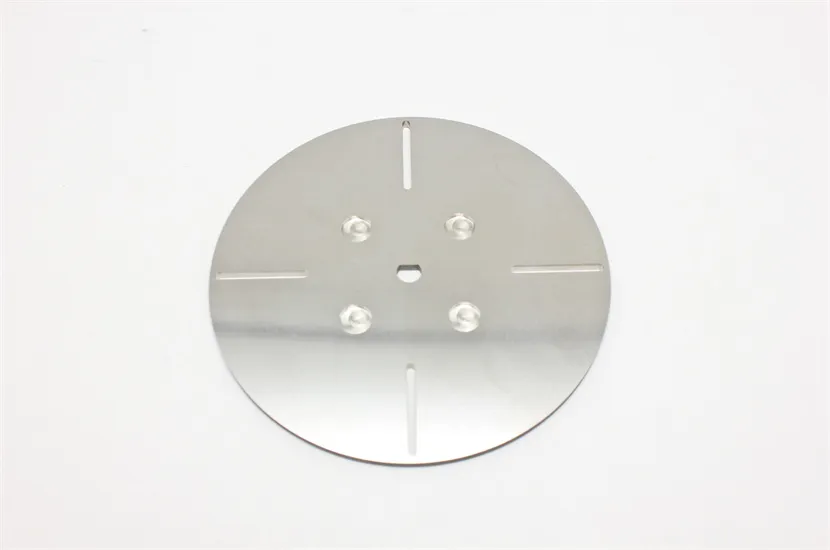
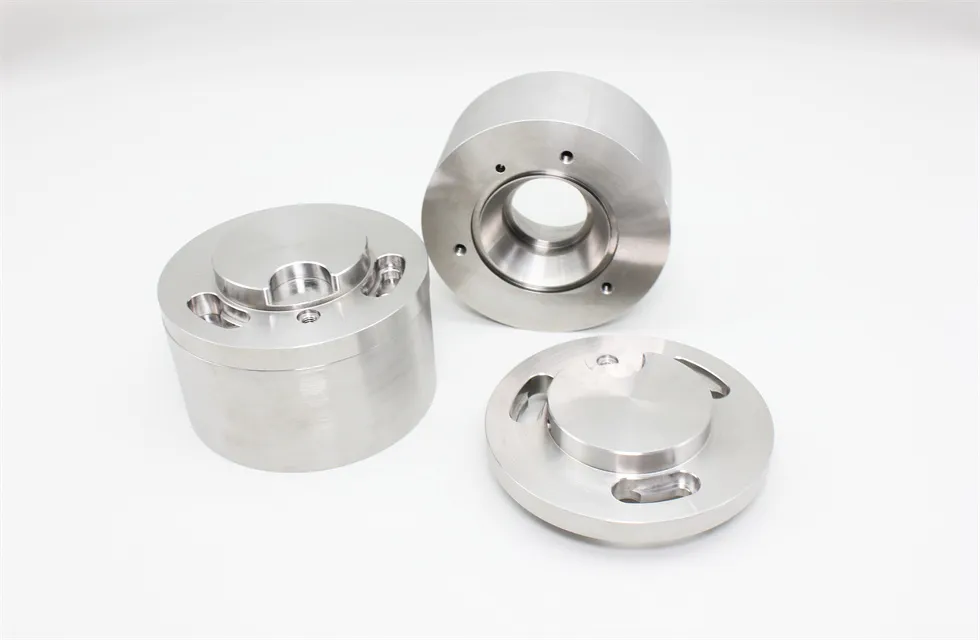
There are many types of high density tungsten alloy products, and different processing methods can produce tungsten alloy products with different shapes, such as tungsten alloy rods, tungsten alloy cylinders, tungsten alloy bars, tungsten alloy blocks, etc. Meanwhile, due to the small volume, high density, high strength, and high hardness of tungsten alloys, they can be applied in many fields. For example, high density tungsten alloys are commonly used in high-temperature structural materials, radiation resistant materials, high-speed cutting tools, and other fields such as aerospace, national defense, nuclear energy, automobiles, and electronics. In addition, high density tungsten alloys can also be used for manufacturing tungsten alloy weights, radiation protection materials, high-density alloys, and so on.

 EN
EN AR
AR FR
FR DE
DE HI
HI IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES ID
ID LV
LV VI
VI HU
HU MS
MS GA
GA BE
BE YI
YI EU
EU