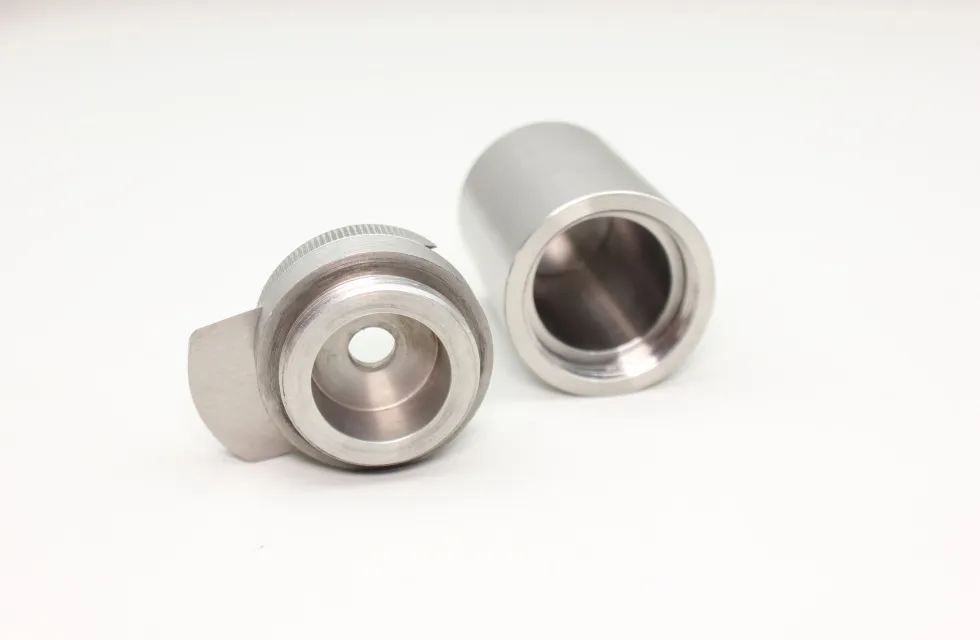
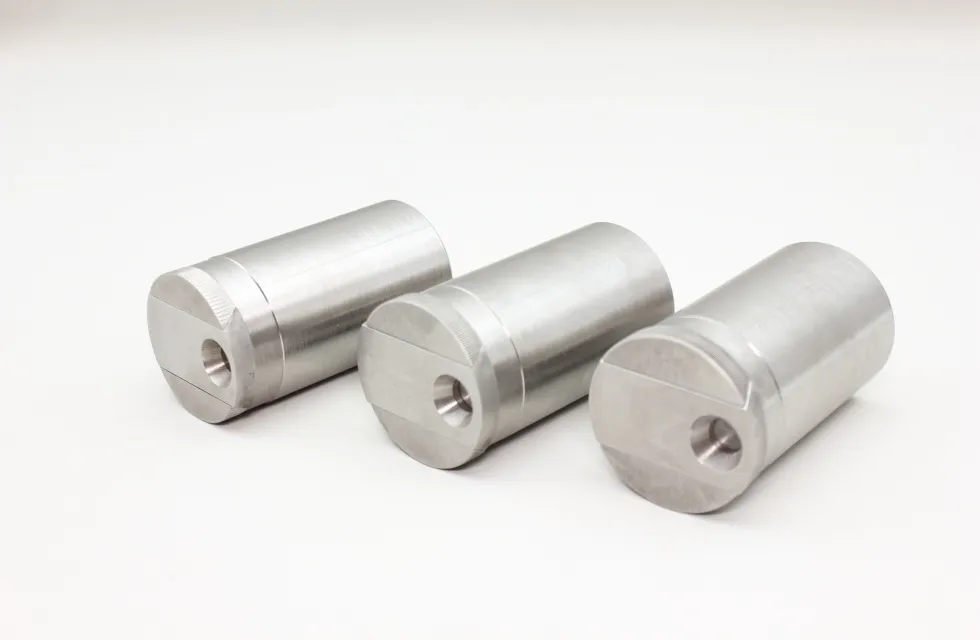
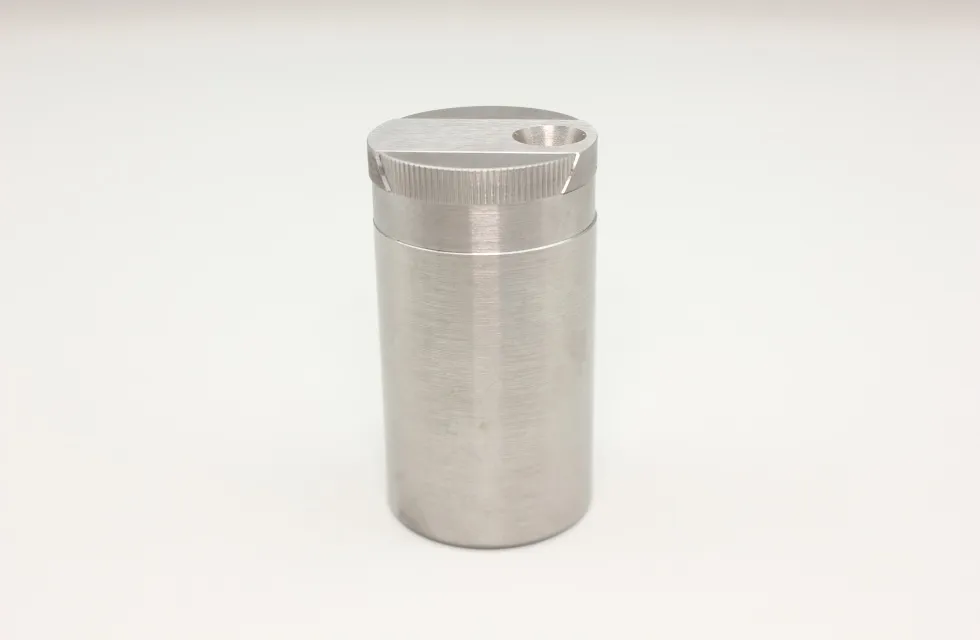
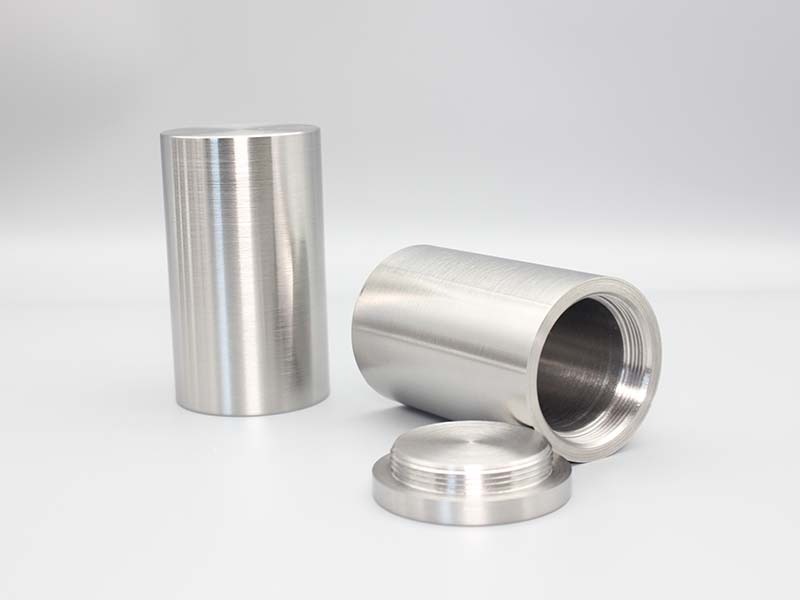
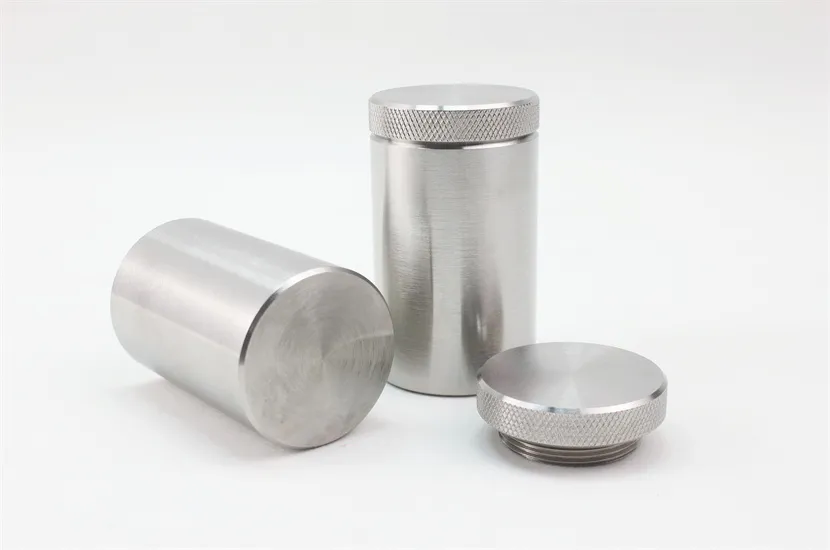
Tungsten shielding for medical radiography
| Payment Type: | T/T |
| Incoterm: | FOB,CIF,EXW,FCA,Express Delivery |
| Min. Order: |
1Piece/Pieces |
Attributes
Model No.: JDTG-TS-025
Brand: ZZJD
Place Of Origin: China
Material: Tungsten
Density: 18.10±0.15g/cm³
Color: Natural
Size: Support customization
PACKAGING & DELIVERY
Selling Units :Piece/Pieces
Package Type : Standard export packing
DESCRIPTION
Here’s a detailed technical and practical comparison between tungsten alloy and depleted uranium (DU) for radiation shielding applications:
Tungsten Alloy vs. Depleted Uranium Shielding: Key Differences
Property Tungsten Alloy (WNiFe/WCu) Depleted Uranium (DU) Winner
Density (g/cm³) 17.0–19.3 18.6–19.1 ≈ Tie
Attenuation Efficiency Slightly lower for high-energy gamma Superior for high-energy gamma/neutrons DU
Toxicity Non-toxic, ROHS-compliant Radioactive (alpha particles), requires licensing Tungsten
Corrosion Resistance Highly resistant (Ni/Fe/Cu matrix) Oxidizes over time (uranium oxide dust risk) Tungsten
Machinability Hard but machinable with carbide tools Softer, but toxic dust requires special handling DU (ease)
Regulations No restrictions ITAR-controlled, requires NRC/DOE permits Tungsten
Thermal Conductivity Moderate (WCu alloys improve heat dissipation) Poor Tungsten
Magnetic Properties Non-ferromagnetic (WNiFe) Ferromagnetic (issues in MRI/labs) Tungsten
Gamma Radiation Shielding Performance
<500 keV: Tungsten matches DU (e.g., Tc-99m, I-131).
>1 MeV (Co-60, Cs-137): DU provides 5–10% better attenuation due to higher Z (92 vs. 74).
Neutron Shielding: DU outperforms (uranium’s fissionable properties help absorb neutrons).
When to Choose Tungsten?
Medical Facilities (PET/CT, radiopharmacy) – Safe for staff/patients.
Commercial/Industrial – Avoid regulatory hurdles.
High-Temp/Chemical Exposure – Won’t degrade like DU.

When DU Might Be Preferred?
Military/Aerospace – Where maximum density is critical (e.g., armor, aircraft counterweights).
High-Energy Physics – Neutron-rich environments (research reactors).
Real-World Considerations
DU Alternatives: Tungsten is now mandated in many civilian applications (e.g., hospital shielding).
Environmental Impact: DU disposal is highly regulated; tungsten is recyclable.
Cost Comparison Example
Shielding Panel (100mm thick, 1m²) Tungsten Alloy Depleted Uranium
Material Cost ~$8,000 ~$3,000
Regulatory Compliance Costs $0 $5,000+ (permits, handling)
Lifetime Maintenance Low High (oxidation monitoring)


 EN
EN AR
AR FR
FR DE
DE HI
HI IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES ID
ID LV
LV VI
VI HU
HU MS
MS GA
GA BE
BE YI
YI EU
EU





